Dr. Shiqing Xu's Lab
Research Activities
Our research aims to develop innovative synthetic methodologies and therapeutic approaches, and apply them to solving pressing problems of biological and medical importance. New synthetic methodologies and strategies (e.g. non-traditional disconnections and C–H functionalization) have great impacts on the discovery of transformational medicines by enabling the rapid and efficient synthesis of novel, diverse, and complex biologically active molecules. New therapeutic approaches (e.g. targeted covalent inhibition and targeted protein degradation) provide new opportunities to address traditionally “undruggable” disease targets. We combine these efforts to achieve the research goal of identifying small-molecule probes and drug candidates that specifically remove/inhibit disease-causing proteins in cells and animal models and ultimately impact human health. Representative research directions include:
- Small-Molecule Approaches to Targeted Protein Degradation for Drug Discovery
Proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC) is a novel technology for targeted protein degradation in precision medicine. PROTACs have many advantages compared to traditional occupancy-based inhibitors, including (i) degrading “undruggable” targets; (ii) weak binders can become potent degraders; (iii) catalytic nature to allow for sub-stoichiometric activity and improved efficacy; (iv) enhanced target selectivity; (v) overcoming drug resistance. We work on the development of small-molecule approaches to targeted protein degradation for drug discovery, particularly focusing on new therapeutics for the treatment of COVID-19 and cancers.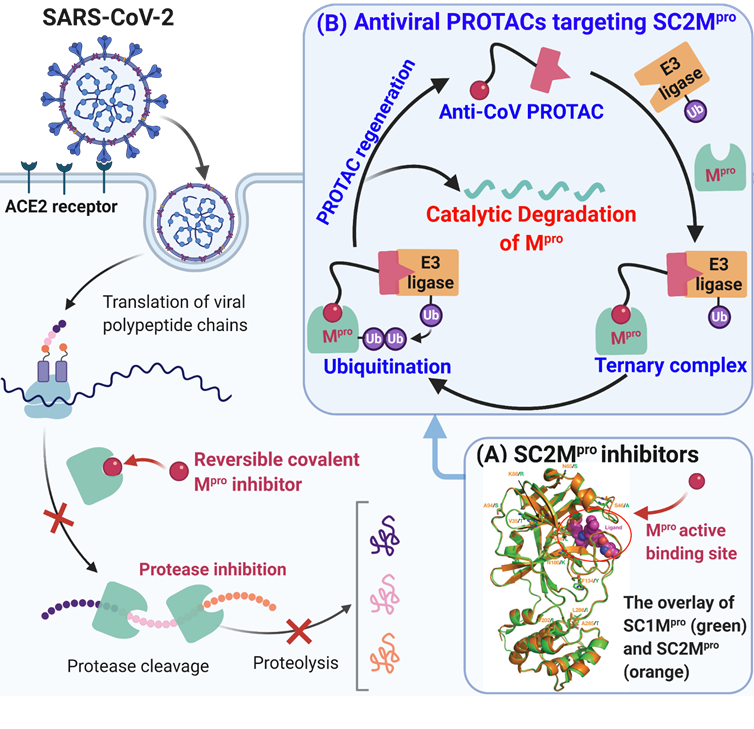
- Late-Stage Functionalization and Its Medical Applications
Late-stage functionalization (LSF), especially of C–H functionalization, offers a fast approach to generate analogs of drugs and drug-like molecules that has great potential to dramatically accelerate the drug discovery process: (i) SAR exploration; (ii) PROTAC development; (iii) chemical biology tool; (iv) metabolite production. We work on the development of novel efficient methods for late-stage C–H functionalization of drugs and drug-like molecules.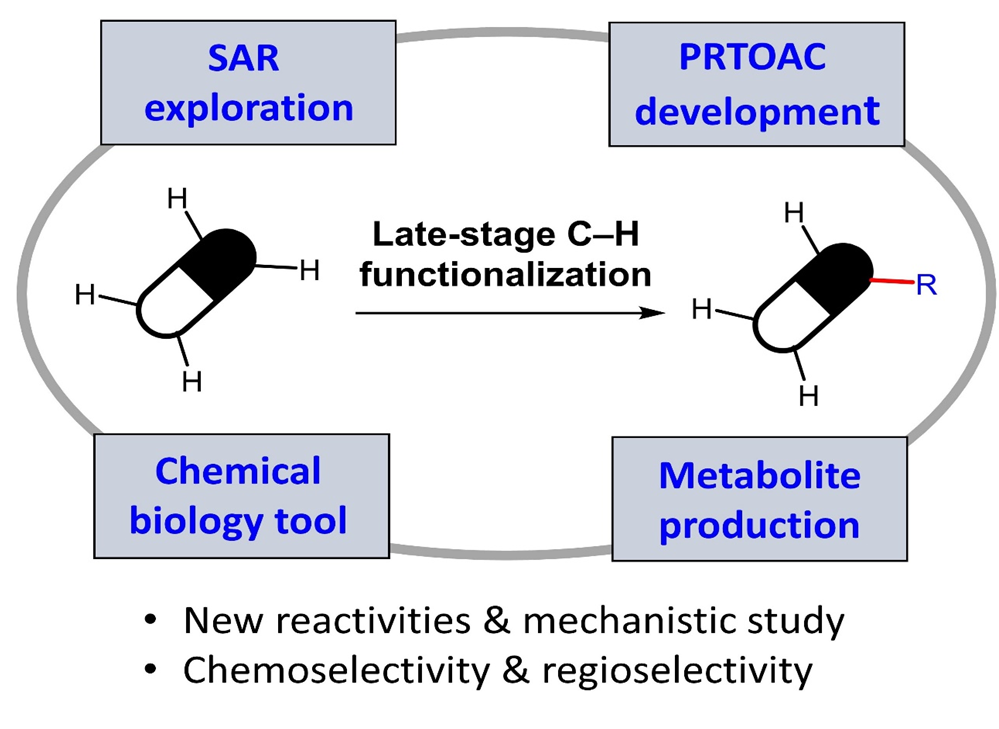
- Organoboron Chemistry and Its Medical Applications
Boron is a unique element that finds versatile utilities not only in organic synthesis, but also in chemical biology and drug discovery. Boron's utilities stem from its vacant p orbital, which enables reversible interactions with various nucleophiles. This flexibility extends to its role as an anchoring element with multiple binding modes during target protein engagement, providing a great opportunity for developing new boron-containing therapeutic agents.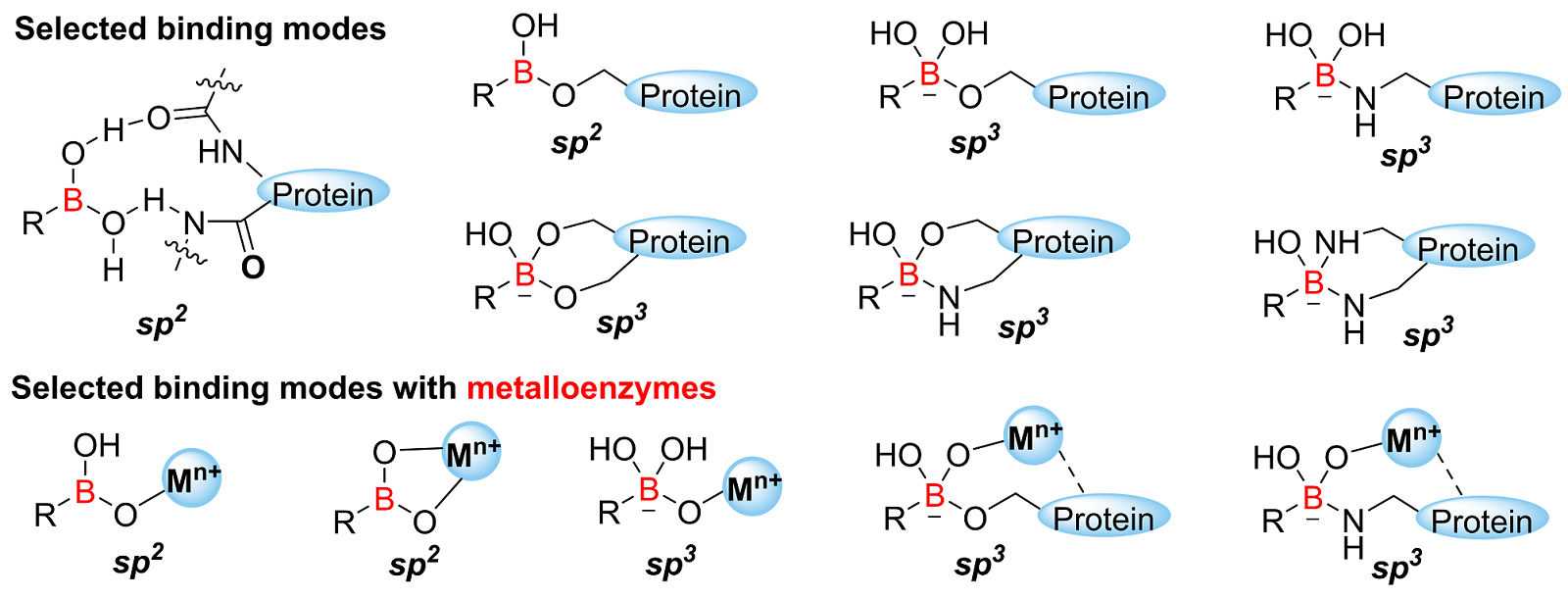
Recent Publications
- Yang, K.; Kuo, S-T.; Blankenship, L.; Sheng, Y.; Sankaran, B.; Li, P.; Fierkee, C.A.; Russell, D.H.; Yan, X.; Xu, S.*; W.R.*. “A Novel Y-Shaped, S–O–N–O–S-Bridged Cross-Link between Three Residues C22, C44, and K61 Is Frequently Observed in the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease.” ACS Chem. Biol. 2023, 18, 449-455.
- Cao, W.; Cho, C.-C. D.; Geng Z. Z.; Ma, X. R.; Allen, R.; Shaabani, N.; Vatansever, E. C.; Alugubelli, Y. R.; Ma, Y.; Ellenburg, W. H.; Yang, K. S.; Qiao, Y.; Ji, H.*; Xu, S.*; Liu, W. R.* “Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors using a novel cell-based assay.” ACS Cent. Sci., 2022, 8, 192-204.
- Alugubelli, Y. R.; Geng, Z. Z.; Yang, K. S.; Shaabani, N.; Khatua, K.; Ma, X. R.; Vatansever, E. C.; Cho, C.-C.; Ma, Y.; Xiao, J.; Blankenship, L. R.; Yu, G.; Sankaran, B.; Li, P.; Allen, R.; Ji, H.*; Xu, S.*; Liu, W. R.* “A systematic exploration of boceprevir-based main protease inhibitors as SARS-CoV-2 antivirals.” J. Med. Chem. 2022, 240, 114596.
- Ma, Y.; Yang, K.; Geng, Z.; Alugubelli, Y.; Shaabani, N.; Vantasever, C.; Ma, X.; Cho, C.; Khatua, K.; Blankenship, L.; Li, P.; Allen R.; Ji, H.*; Xu, S.*; W.R.* “A multi-pronged evaluation of aldehyde-based tripeptidyl main protease inhibitors as SARS-CoV-2 antivirals”. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 240, 114570.
- Ma, X.; Alugubelli, Y.; Ma, Y.; Vantasever, C.; Scott, D.; Qiao, Y.; Yu, G.; Xu, S.*; W.R.* “MPI8 is Potent against SARS-CoV-2 by Inhibiting Dually and Selectively the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease and the Host Cathepsin L”, ChemMedChem 2022, 17, 202100456.
- Yang, K.; Leeuwon. S.; Xu, S.; Liu, W. R*. “Evolutionary and structural insights about potential SARS-CoV-2 evasion of nirmatrelvir”. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 8686-8698.
- Cho, C.; Li, S.; Yang, K.; Lalonde, T.; Yu, G.; Qiao, Y.; Xu, S.*; W.R.* “Drug Repurposing for the SARS-CoV-2 Papain-Like Protease”, ChemMedChem 2022, 17, e202100455.
- Yang, K.; Kuo, S-T.; Blankenship, L.; Geng, Z.; Li, S.; Russell, D.; Yan, X.; Xu, S.*; Liu, W. R*. “Repurposing Halicin as a Potent Covalent Inhibitor for the SARS-CoV-2 Main Proteas”. Current Research in Chemical Biology (CRCHBI), 2022,
- Li, S.; Yang, K.; Blankenship, L.; Xu, S.*; Wang, H.*; Liu, W. R.* “An Enhanced Hybrid Screening Approach to Identify Potent Inhibitors for the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease from the NCI Compound Library”. Chem., 2022, 816576.
- Cheng, H.; Yang, T.; Edwards, M.; Tang, S.; Xu, S.*; Yan, X*. “Picomole-scale transition metal electrocatalysis screening platform for discovery of mild C–C coupling and C–H arylation through in situ anodically generated cationic Pd.” Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 1306-1312.
- Huang, K-H.; Ghosh, J.; Xu, S.*; Cooks, R. G.* “Late-Stage Functionalization and Characterization of Drugs by High-Throughput Desorption Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry”. ChemPlusChem 2022, 87, e202100449.
- Fu, X.; Qi, Q.; Xu, S.*; Negishi, E. “Chemo-and Stereoselective Dearomative Coupling of Indoles and Bielectrophilic β-Imino Boronic Esters via Imine-Induced 1,2-Boronate Migration”. Lett. 2021, 23, 8984-8988.
- Yang, K.; Ma, X.; Ma, Y.; Alugubelli, Y. R.; Scott, D. A.; Vatansever, E. C.; Drelich, A. K.; Sankaran, B.; Geng, Z.; Blankenship, L. R.; Ward, H. E.; Sheng, Y.; Hsu, J. C.; Kratch, K. C.; Zhao, B.; Hayatshahi, H. S.; Liu, J.; Li, P.; Fierke, C. A.; Tseng, C.-T. K.;* Xu, S.*; Liu, W. R.* “A Quick Route to Multiple Highly Potent SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors.” ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 942-949.
- Morse, J. S.; Lalonde, T.; Xu, S.*; Liu, W. R.* “Learning from the past: possible urgent prevention and treatment options for severe acute respiratory infections caused by 2019‐nCoV.” ChemBioChem 2020, 21, 730-738.
- Tharp, J.M.; Hampton, J.T.; Reed. C.A.; Ehnbom, A.; Chen. P.C.; Morse, J.S.; Kurra, Y.; Perez. L.M.; Xu, S.*; W.R.* “A Phage-Displayed, Active Site-Directed Ligand Evolution Technique”, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1392.
*as Corresponding Author
Google Scholar: https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=E7Jq2PQAAAAJ&hl=en